|
Before
detailing the activities developed by ONS in 2003, an overview
will be given of the evolution of the physical generation and
transmission segments of the NIS, a direct result of actions by
ONS, as well as the follow-up of the evolution of the energy demand
in the system.

a)
Generation System
During 2003, the NIS incorporated 2,870.8 MW of new generation
offer broken down into 2,275.6 MW from hydro plant production
and the rest - 595.2 MW - from thermal plants representing a total
of 37 new generation units. This increase added a 3.8% growth
in the installed capacity in relation to the same period of the
previous year. The new generation units represent a 6.5% increase
in number in relation to the 566 units in operation at the end
of 2002.
By the end of 2003, the NIS installed capacity reached 77,321
MW, roughly 66,321 MW from hydro plants and 11thousand MW from
thermal generation units (including 2,007 MW from nuclear plants
and 50% of the installed capacity of the Itaipu Complex - that
belongs to Brazil - equivalent to 6,300 MW). The total number
of existing generation units was 603 by the end of 2003. To obtain
the total available production capacity these values must be added
to the energy imported from Argentina - 2,178 MW and Itaipu –
4,100 MW contracted from ANDE/Paraguay.

b)
Transmission System
General
Aspects
The
Brazilian Transmission System registered a growth rate in terms
of its extension, of 7.1% in relation to 2002, adding 5,136 km
of new T lines. With entry of 12 new substations, a 3.9% increase
was recorded over the 306 installations in 2002, reached a grand
total of 316 substations. An increment of 9,704 MVA corresponding
to 5.8%, in the NIS transformation capacity, was also demonstrated
in relation to the previous year.
Structure
of the Available Capacity in the NIS (MW)
| |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
| National
Hydro |
54,693.7 |
57,533.7 |
60,021.0 |
| Itaipu
(1) Hydro |
6,300.0 |
6,300.0
|
6,300.0 |
| Conventional
Thermal |
5,028.2
|
7,002.0
|
7,219.2
|
| Thermal-nuclear |
1,966.0 |
2,007.0
|
2,007.0
|
| Emergency
Generation |
- |
1,827.3
|
1,773.8
|
| Importation(2) |
1,192.0 |
2,192.0 |
2,178.0 |
| Total
|
69,179.9 |
76,862.0 |
79,499.0 |
Data
of 12/31/2003
(1)
Includes only the Brazilian portion of the Itaipu Binational Complex.
Total value of energy contracted by integrant NIS companies: 10,074
MW/year.
(2)
Refers to maximum import capacity from Argentina, Uruguay and
ANDE - Paraguay.
The transmission system at voltages between 230 kV and 750 kV,
represented in December of 2003, a total of 77,642 km consisting
of 780 transmission circuits and 175,916 MVA of transformation
capacity installed at the 316 substations in the System.
The following tables show the evolution of the transmission system
and the transformation capacity of the Main Transmission Network
in the period 2001 –2003:
Transmission
Network
| Voltage
(kV) |
2001 |
2002
|
2003
|
| 230
|
32,537.3
|
32,997.4
|
33,999.7
|
| 345
|
9,023.5
|
9,021.0
|
9,021.0
|
| 440
|
6,667.5
|
6,667.5
|
6,667.5
|
| 500
|
17,510.1
|
19,525.2
|
23,659.0
|
| 600
CC |
1,612.0
|
1,612.0
|
1,612.0
|
| 750
|
2,683.0
|
2,683.0
|
2,683.0
|
| Interconnected
System |
70,033.4
|
72,506.1
|
77,642.1
|
Transformation
Capacity – Voltages greater than 230 kV (1)
| Region |
2001
|
2002 |
2003 |
| SE/CO
|
105,570.9
|
107,370.9 |
113,180.9
(2) |
| S
|
24,785.7 |
26,678.7
|
28,172.7
(1) |
| S/SE/CO
|
130,356.6 |
134,049.6 |
141,353.6
(2) |
| N
|
9,953.9 |
10,183.9
|
10,483.9
(2) |
| NE
|
19,495.5 |
21,978.8 |
24,078.8
(2) |
| N/NE
|
29,449.4 |
32,162.7 |
34,562.7
(2) |
(1)
The installed transformation capacity contemplates only those transformers with a transmission and/or load attendance function.
Exclusions include elevator transformers located at Generator
Units and units used specifically with Synchronous and Static
Compensators.
(2)
On 12/08/2003, FURNAS de-activated Transformer number T2B1 - 345/138
kV, 225 MVA, in the ADRIANOPOLIS Substation that operated with
a temporary configuration.
Inter-regional
Interconnections
The
energy transfer capacity between regions was increased due to
the entry into operation of reinforcements made in the interconnections
that act as virtual power plants. Among the important events and
aspects:
•Implantation
of the 500 kV Tucurui/Marabá C3 transmission line and the
Marabá/Açailândia/Imperatriz C1, Açailândia/Presidente
Dutra C1 and Presidente Dutra/Teresina C2 transmission lines that
increased the export capacity of the North region and the limits
for receiving power from the Northeast region by about 300MWmed.
•
In 2003, the Northeast region began to operate, directly integrated
to the Southeast region, with the entry of the Serra da Mesa/Rio
das Éguas/Bom Jesus da Lapa/Ibicoara/Sapeaçu - 500
kV transmission line, providing an increase in a power reception
capacity of 600 MWmed.
•The
beginning of the first steps of the expansion work on the North-South
Interconnection, contemplating the 500kV transmission lines at
Serra da Mesa - Samambaia C3 and Serra da Mesa - Gurupi - Miracema
C2, besides the compensation series at Samambaia. This work permits
the raising of transmission limits between the North and Southeast/Midwest
regions by 800 MWmed.
•With
the implantation of the double circuit 500 kV Ibiúna /
Bateias transmission line, another link was created in the South
– Southeast interconnection increasing the interchange capacity
between these two regions. This line adds an increased reception
capacity by the Southeast by 1,500 MWmed and about 1,000 MWmed
by the South region.
Regional
Supply Installations
Regarding
the improvement of the inter-regional supply capacity, the following
entries of new installations is highlighted:
•
In the Rio Grande do Sul area: transmission lines - 230 kV Caxias
2 / Caxias, Gravataí / Porto Alegre 6, a new substation
at Taquara 230/138 kV and a 230 kV Taquara / Caxias transmission
line;
•
In the Curitiba area: a new substation at Campo Comprido and new
230 kV Cidade Industrial / Gralha Azul and Cidade Industrial /
Campo Comprido transmission lines;
•
At Fortaleza: circuit conversion to 500 KV at Milagres / Quixadá
/ Fortaleza and a 230 kV Cauípe / Fortaleza C2 transmission
line;
•
In the central area of Minas Gerais, a new substation at Vespasiano
that sectioned the 500 kV Neves-Mesquita transmission line;
•
In the Rio de Janeiro/Espírito Santo area: transformation
increases at the Adrianópolis 500/345 kV and Vitória
345/138 kV substations;
•
In the São Paulo area: a new station at Avaré and
the transformation increases at the Tijuco Preto 750/500 kV, Bandeirantes
345/230 KV and Interlagos 345/230 kV substations;
Installations
to viabilize the integration of power plants:
A
new transmission line - 230 kV Jauru-Cairo - in Mato Grosso, integrating
the NIS with the Jauru and Guaporé hydro plants as well
as other smaller hydroelectric plants in the state.

The
total electric energy consumption of the NIS, including losses
in the transmission and distribution systems, (excluding energy
imports), was recorded at 41,780 Mwmed - about 5.3% higher than
in 2002.
The highest verified demand in the system in 2003 - representing
the maximum integralized power on an hourly basis during the peak
load period was recorded at 53,515 MWh/h, occurring at 19:00 hours
on May 22, 2003 – a value 5.7% greater than registered in
the previous year.
The
values, dates and times for the maximum demand by region and the
corresponding growth rates over the 2002 results are shown as
follows:
Region
|
Total
Consumption MWmed |
Growth
% |
SE/MW |
26,258
|
5.5
|
South |
7,236
|
2.3
|
Northeast |
6,388
|
7.4
|
| North |
2,829
|
6.0
|
| Region |
Demand
MWh/h |
Date
of event |
Time |
Growth
% |
| SE/MW |
33,720
|
22/04 |
19:00
|
6.0
|
| South
|
9,900
|
23/09 |
20:00 |
3.8
|
| Northeast
|
7,774
|
04/12 |
20:00 |
3.7
|
| North |
3,249
|
29/11 |
22:00 |
10.2
|


By
the end of 2003, the number of Generation, Distribution and Transmission
Agents totaled 128, a growth of 6.67% over the total for 2002.
The largest increase was seen in the Transmission segment that
grew from 20 to 28 associate agents at ONS, mainly due to new
investments in the sector. In the Generation category, two new
agents were brought in raising the total to 78 members. One new
Free Consumer also joined the operation - Fibraplac – who
is connected to the Main Transmission Network at Rio Grande do
Sul.

Among
the alterations made in the regulatory legislation in 2003, the
following events and highlights were recorded:
a)
ANEEL authorization for temporary use - until reviewed at a public
audience - of the Grid Procedures Module 14 - “Ancillary
Services” and Module 8 - “Daily Electro-energetic
Programming” as well as the second revised version of Module
10 – “Manual of Operation Procedures” in compliance
with Resolution 675/03.
b) First use by ONS of the Grid Procedures Module 19 – “Identification
and Treatment of Non-conformities”, according to a directive
from ANEEL.
c) Issuance of the National Waters Agency – ANA Resolution
434/03, authorizing the temporary reduction of the minimum water
flow limit at Sobradinho, from 1,300 m3/sec. to 1,100 m3/second.
The aim was to permit a greater thermal energy dispatch in the
Northeast region and maximize power transference from the Southeast
and North regions, in order to recover the reservoir water levels
in view of the unfavorable rainfall conditions verified in this
region.


d) With the objective of establishing regulatory guidelines for
the procedures indicated in GCE Resolution 109, to give greater
safety to the energetic operation, The CNPE – the National
Council for Energy Policies issued Resolution 10/03, regulamented
by ANEEL Resolution 686/03, establishing among other things, procedures
related to the use of Risk Aversion Curves - CAR. In the imminence
of the curves being reached, ONS must dispatch complementary thermal
generation in order to prevent the water storage levels from reducing
below the limits defined by the Risk Aversion Curves. In this
situation, when emergency plants are dispatched, these plants
will not be considered when determining the MAE energy prices.
However, if in fact the Curve is reached, dispatch from these
plants will be considered in the MAE energy prices.
e) As a consequence of the hydrologic conditions, in the South,
resulting in very reduced water levels at the reservoirs in the
region, especially on the Iguaçu River, ONS conducted studies
in collaboration with energy companies operating in the area in
order to establish new Risk Aversion Curves. These new values
were submitted to ANEEL and subsequently approved after the Public
Hearing held to present the altered values.
f) Issuance of the CNPE Resolution 03/03 that defined the directives
for conducting auctions of surplus energy from generation concessionaires
and authorized agents; issuance of ANEEL Resolution 353/03 establishing
the general conditions for the exclusive sale of residual electric
energy resulting from the release from the Initial Contracts or
Equivalent Contracts Agreements. Responsibility falls on ONS and
the distribution agents to issue a Technical Report to MAE presenting
the remaining capacities associated with the connection points
used for different proponent purchasers as well as the amount
of electric energy in question.
g)
Special highlight must be given to the issuance by the Federal
Government, in December 2003, of the Provisional Measures 144
and 145 that establish a new institutional milestone in the Brazilian
Electric Sector which will be regulamented in 2004.


The
operation of the National Interconnected System - NIS, throughout
2003, ran well within the limits established in the Grid Procedures.
The
activities conducted by ONS, together with sector authorities
and with the support of sector Agents, aided in minimizing operational
costs and at the same time, maximize the safety of the electric
supply. Furthermore the joint efforts made helped the Operator
observe the constraint limits imposed by the multiple uses of
water resources and the actual operational limitations of the
installations of the system. ONS obtained a high degree of success
by simultaneously complying with all these objectives through
its coordination and control activities of the NIS while trying
to maintain the goal of consistent systemic optimization.

The
safety conditions of the electric energy supply were evaluated
based on probabilistic analyses that estimated the risk of occurrence
of energy deficits. These studies were complemented by deterministic
studies based on biannual risk aversion curves – CAR.
The regional water storage level positions, in relation to the
curves, were monitored and published continuously. They aided
the National Operator to establish interregional energy interchanges
and the thermal generation dispatch in order to minimize costs
and maintain acceptable reliability standards, in view of the
recorded hydrological conditions and the energy consumption behavior
of each region.
In the Southeast/Midwest region, the hydrologic conditions presented
a normal profile (92.4% long-term average). This allow ed for
the maintenance, throughout 2003, of the regional water storage
values at levels far above those determined by the Risk Aversion
Curves. During most of the year, this region exported energy to
the Northeast and South, thus contributing to the equalization
of the power supply conditions between the different regions of
the country.
The South region experienced unfavorable inflows between September
and November with a significant reduction of water levels at the
reservoirs along the Iguaçu River. This fact lead ONS to
maximize the energy supply from the Southeast to this region in
order to help maintain the water storage levels above the limits
set by the Risk Aversion Curves for the region.
Load
demand was supplied within the normal conditions in the period.
There were occurrences of spillages at Tucuruí during the
wet period following the controlled depletion of the reservoir
during the dry season guaranteeing the necessary power supply
to the regional market and the transfer of energy to the Northeast,
without violating the Risk Aversion Curve storage levels established
for this region.
To facilitate entry of the second stage operation of the Tucuruí
plant, the water level at the reservoir was lowered over the second
half of 2002. In January of 2003, in order to recover the water
level, ONS ordered importation, by the North region, of 120 MWmed
from the Southeast region.
In 2003, the Northeast registered an average inflow of 71.4% of
the long-term historic average. However, between May and September,
inflows fell significantly to only 66%. This situation demanded
special attention from ONS in the management of the energetic
resources. The strategy adopted was to maximize the interchange
received from neighboring regions which helped keep the water
levels in the Northeast above the Risk Aversion Curves limits.
In terms of annual values, this strategy resulted in water storage
in the region in the order of 15,100 MWmed, roughly equal to 30%
of the storage capacity of the entire region.
Between September and December of 2003, the inflows in the region
were unfavorable demonstrating values of only 55% of the historic
average. This resulted in the reduction of the safety margin related
to the water storage levels compared to the respective Risk Aversion
Curve. As such, in the first two weeks of December, the natural
gas powered thermal units were dispatched at maximum generation.
The emergency thermal plants, at a much higher operational cost,
were also put on-line during the last few days of the year –
on December 27th. This integrated operation policy, bringing together
various System resources, contributed to the overcoming of adverse
hydrological conditions at the lowest possible cost while protecting
the water storage level in the region that was at only 14% of
the maximum capacity by year’s end – equal to the
limit set by the Risk Aversion Curve for the region.
 > >
NIS
- 2003: Participation-by-source of verified energy generation
and imports - shown in %:


Looking
at the NIS electric supply conditions, in 2003 the System operated
well within the criteria established in the Grid Procedures when
examining continuity, reliability and supply quality. There were
no major disturbances recorded in the period thanks to the circuit
loading and dispatch polices used during the year by ONS. An adequate
level of compatibility was achieved between supply safety and
energetic optimization and the almost perfect functioning of the
safety and protection schemes whose job was to minimize the eventual
propagation of equipment shutdowns and the risk of outages in
the System.
Mention must be made of the improvements that were made in the
operative safety of the NIS in spite of the fact that the complexity
of the System increased due to the integration of various large
sized installations and the expansion of the interconnections
among the regions. The NIS received 37 new generation units and
12 substations as well as more than 5,000 km of transmission lines,
close to 2,000 Mvar of capacitor series and 5,000Mvar of reactors,
equipment that required the running of operational tests and commissioning
simulations – all of which demanded the closest scrutiny
by ONS beginning with the preliminary access request and pre-operational
studies. This work depended on very close interaction between
the National Operator and sector agents, owners and operators
of the new installations; work that included intense monitoring
during the initial equipment start-up operations, when a high
probability of problem incidents normally occurs.
In 2003, operative safety improvements made in the NIS can be
verified by looking at the number of disturbances that, significantly,
did not provoke load cuts of any kind – more than 80%. Even
when operating under conditions close to the transmission system
limits, the system supported multiple contingencies very well
while complying with the safety and quality requirements. The
verified performance recorded for frequency of the system was
higher than the previous year. While in 2002, there were 10 events
in which the frequency reached a value less than 58.5Hz; in 2003
this value was repeated in only four disturbances, involving exclusively
the North/Northeast subsystem.
The detailing of institutional activities conducted by the National
Operator and the results obtained by these actions is presented
in item 5.4 of the report under the title – Electro-energetic
Management.

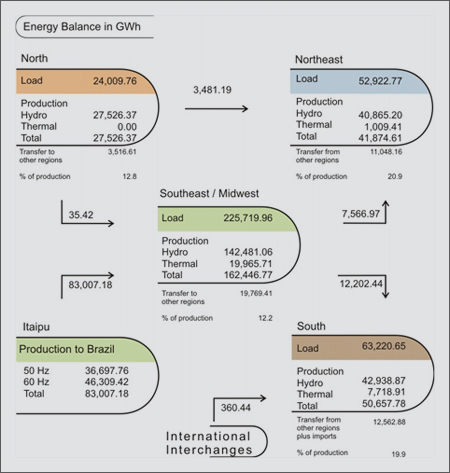
The
total electric energy consumption in the NIS, including losses
in the transmission and distribution systems was recorded at 41,780
MWmed, approximately 5.3% higher than recorded in 2002.
The
first of the following Tables presents the NIS energy load corresponding
to all of the energy consumed including technical losses, in GWhours,
for the period 2001 – 2003.
The verified load peak, (see the second table below), representing
the maximum integralized power on an hourly basis at the load
peak period , expressed in MWh/h, is presented for the period
2001 – 2003.
Região |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
var.% |
SE/MW |
202,990.8
|
213,857.2
|
225,720.0
|
5.5
|
SOUTH |
60,660.2
|
61,824.6
|
63,220.7
|
2.3
|
NORTHEAST
|
46,341.0
|
49,286.1
|
52,922.8
|
7.4
|
NORTH |
20,412.0
|
22,526.7
|
24,009.8
|
6.6
|
SIN
(MWmed) |
37,752.0
|
39,658.8
|
41,780.4
|
|
Load
Demand in MWh/h
|
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
var/03/02
|
|
35,776
|
31,810
|
33,720
|
6.0
|
Day/Mon.
|
24/apr |
16/oct |
24/apr |
|
Time
|
19
|
20
|
19 |
|
|
10,059
|
9,539
|
9,900
|
3.8
|
Day/Mon. |
21/may |
4/jun |
23/sept |
|
Time |
20 |
19
|
20
|
|
|
44,865
|
41,256
|
43,353
|
5.1
|
Day/Mon. |
24/apr |
15/ouct |
22/may |
|
Time |
19 |
20 |
19 |
|
|
7,745
|
7,500
|
7,774
|
3.7
|
Day/Mon. |
17/feb |
21/dec |
4/dec |
|
Time |
21
|
21
|
20 |
|
NORTH |
2,881
|
2,949
|
3,249
|
10.2
|
Day/Mon. |
12/may |
20/aug |
29/nov
|
|
Time |
20
|
20
|
22 |
|
|
10,538
|
10,285
|
10,891
|
5.9
|
Day/Mon. |
17/feb |
7/dec |
26/nov |
|
Time |
21
|
21
|
20 |
|
|
55,099
|
50,759
|
53,515
|
5.4
|
Day/Mon. |
24/apr |
15/ouct
|
22/may |
|
Time |
19
|
20
|
19 |
|

The Action Plan, subject to approval by ANEEL, is a fundamental
part of the ONS planning system, elaborated every year based on
a three-year horizon in consonance with previous cycles.
The Action Plan covering 2003/2005 contemplates the environmental
conditioning factors of the Brazilian Electric System –
BES; the strategic challenges faced by ONS in this period; the
permanent commitments of the National Operator and the activities
focusing on achieving the strategic challenges including directives
and associated projects.
The strategic challenges listed below have been based on the need
to fulfill the permanent commitments of the Operator and take
into consideration the environmental conditioning factors of the
energy sector referred to above:
a) Maintain the NIS at a level of optimized performance;
b) Guarantee the electric safety of the NIS;
c) Assure the efficient management of the Grid Procedures and
operational relations with all sector Agents;
d) Elaborate proposals and participate in the process of change
in the BES;
e) Guarantee and adequate evolution of the methodologies and technical
management processes of the NIS;
f) Assure the evolution of the institutional relations within
the BES and the society so as to widen knowledge of the role of
ONS;
g) Consolidate the bases and instrumentalize the corporate management
of ONS.
The total amount of the Action Plan Budget for 2003 was approved
by the Administrative Board and by ANEEL through Resolution 310,
published in the Diário Oficial on July 01/2003, originally
estimated at R$ 31,094.2 thousand.
Through Resolution 518 dated 10/03/2003, ANEEL approved a revision
of the Budget for 2003 raising the amount to R$ 32,447.5 thousand.
Of this revised value, a total of R$ 31,641.5 thousand was effectively
spent, equivalent to 97.5% of the Revised Budget.
The ONS Action Plan for the period 2003/2005, contemplates not
only the strategic challenges imposed by the environment of the
energy sector, but also the permanent commitments of the Operator,
based on 15 projects briefly shown below, including the results
achieved in 2003.
PROJECT
1
Development
of the Strategic
Management Model
The
development of this model aims at preparing ONS to face the challenges
associated with the increased complexity of the NIS operation
in regard to the institutional and organizational improvements.
In this project the concept-reference was developed consisting
of ONS characteristics and organizational values, inherent responsibilities,
institutional prerogatives and the requirements for healthy external
relations. The process of detailing the “Organizational
Systems” was initiated in this first phase targeting general
improvement of management activities at ONS.
PROJECT
2
Development
of an Agent Relations System
The
objective of this Project is to create an integrated model for
Information Management and Agent Relations and to develop and
implant a general Information System to improve the quality of
service provided by the Operator. Among the results of the project,
mention must be made of the implementation of the new SIGA Information
System in 2003.
The
modeling of the system and its functional specifications as well
as the definition of the implantation strategy were among the
major landmarks reached in 2003 . The implantation of the GED
– Electronic Documentation Management System is still in
progress.
PROJECT
3
Development
of Models and Processes
for Integrating New Agents to the NIS
This
Project aims at bettering the relationship between ONS and sector
Agents that will be connecting to the NIS. The objective is to
develop and establish, for each new Agent, to facilitate his functions
in the sector, an outline of the individual responsibilities during
the Access Request Process and the final integration of the agent
installations to the System, describing the procedures and highlighting
Agent participation in the process of the operation of the system
after his entry to the operation. This project designs actions
that will guarantee integration of the new installation, in the
safest possible manner, in compliance with requirements outlined
in the Grid Procedures.
Procedures for coordinating the process and the step-by-step process
accompanying the integration of new installations were systematically
established to aid all sector Agents.
PROJECT
4
Implantation
of an Operational
Auditing Routine
This project contemplates the activities needed to implant an
operational audit procedure at ONS. The main purpose of this routine
is to verify the total compliance of all operational processes
as established in the Grid Procedures.
A manual entitled “Manual for Operational Audit Procedures”
was elaborated. These procedures were used to audit the Biannual
Telecommunications Plan, the Disturbance Analyses routines, the
Monthly Operation Program and the Quarterly Planning of the Electric
Operation.
PROJECT
5
Grid
Procedures Management
This project was designed to detail the technical processes and
to elaborate manuals containing the identification of responsibilities
of all sector Agents, in relation to the ONS activities as outlined
in the Grid Procedures. These procedures are understood to be
a set of rules and technical processes, necessary and indispensable,
so that the National Operator may fully exercise all institutional
attributions. By the end of 2003, all 23 Modules of the Grid Procedures
were approved by ANEEL for provisional use.
PROJECT
6
Improvement
of the Models and Processes of
Corporate Management
This Project targets the upgrading and general improvement of
all corporate management practices principally in regard to the
functions of the Corporate Management System and the Economic-Financial
Management System. It focuses on improving the managerial processes
in the Competences Management System of the ONS technical and
management personnel.
In 2003 the final stages of the People Soft, version 7, Corporate
Management System were concluded as well as the elaboration of
the basic structure for the Integrated Economic-Financial Planning
System.
PROJECT
7
Improvement
of the Operational and Corporate Infrastructure
for Information Technology and Telecommunications
This Project was designed to provide ONS with the necessary conditions
so that the Information and telecommunications operational and
corporate systems can guarantee a high level of productivity and
efficiency in all respective processes.
Highlights in 2003 include: integration of the Technical Database
with the Real Time Database, the evaluation of the existing computational
systems and the upgrading and expansion of the telephone systems
at ONS.
PROJECT
8
Improvement
of the Operation Planning and Programming Models,
Methodologies and Processes
The work focuses on bettering the methodologies and improving
the efficiency of the models and processes associated with the
operation programming and planning.
In 2003, work was finished on the development of the SIPPOE Project
– the system integration model – which is now undergoing
implantation. Furthermore, in 2003, the concept of risk aversion
curves was incorporated in the mid-term optimization model –
NEWAVE.
The SADEPE system is still undergoing development and will e used
for gathering outside information needed by ONS for the elaboration
of the energetic operation planning. Highlights include the beginning
of the development of a new short-term programming model called
DESSEM. Finally, in 2003, purchase was made of the license to
use and absorb the SDDP -an optimization model, with a detailed
representation of the plants, to be used in energy operation planning.
PROJECT
9
Improvement
of the NIS
Operational Safety Conditions
The objective of this Project is to increase the operative safety
of the National Interconnected System – NIS when facing
multiple contingency events and single contingencies when provoked
by multiple shutdowns.
The Project comprehends the National System of Safety Control
which was expanded in 2003 to include Safety Zone 1- ECS de Assis.
Additionally, Project highlights include the implantation of basic
tests as part of the Post-fault Analysis System and the beginning
of the preventative maintenance programs for the ECS already set
up; continuity of the studies for the implantation of long-term
oscilographic systems; improvement of the models used to evaluate
voltage stability and dynamics; a computational system for voltage
coordinated control and finally, optimization of computational
tools used to study system recompostion.
PROJECT
10
Improvement
of the Models
and Processes of Load Forecasting
The main target is to streamline the relations between ONS and
the Agents involved in forecasting load. The purpose was to comply
with all guidelines laid down in Module 5 of the Grid Procedures,
and includes the introduction to computational environments that
facilitate the reception and treatments of data as well as the
technological and computational advances needed for load forecasting
for electric and energy studies. Highlights include the implementation
of the ANNSTLF -Artificial Neural Network Short Term Load Forecaster,
used to make hourly forecasts for 1 to 35 day periods.
PROJECT
11
Development
and Implantation of
Hydro-meteorological Management Models and Processes
This project includes work on three main objectives focusing on
input, processes and products that support the development of
actions related to hydro-meteorology within the scope of ONS interests
– namely:
• Expand access and incorporate more hydro-meteorology data
so as to build a historical data file and improve the process
used to update this information at ONS. Important work done includes
the Revision Project for Natural Water Flow Series in the main
hydrologic basins of the NIS. This revision now includes data
for the period of 1931 to 2001. The work was carefully followed
by ANEEL, ANA, CCPE/MME and generation Agents and marked the incorporation
of information on the consumption of water for multiple uses in
the streamflow series of the different basins in the system. It
marked the improvement in the evaluation of hydraulic resources
not only for planning the NIS operation but also for expansion
planning and extra-sectorial studies, associated with hydraulic
resources management.
• Organize the processes utilized in the hydro-meteorological
area, highlighting the issuance of recommendations for the improvement
of hydrometric and reservoir level monitoring at the basins in
the NIS when considering the multiple use of water resources.
• Innovate products and processes at ONS in the hydro-meteorological
area, incorporating new technologies and scientific advancements.
PROJECT
12
Operational
Integration of
New Installations
This Project was designed to insure that integration of new installations
in the NIS is done in the safest possible manner and that all
pertinent information related to the start-up of operations be
made available to all interested Agents. Included in this information
package are directives for elaborating the first operations instructions,
guidelines for pre-operational studies and a set of procedures
for holding commissioning simulations, all designed to guarantee
the safety and reliability of the NIS.
In 2003, 40 pre-operational studies were developed for integrating
new transmission and generation installations. This was an increase
of 91% in relation to the 21 studies held the previous year. Highlights:
6 thermal plants: 5 hydro plants; nearly 5,000 km of new 500kV
transmission lines; 12 large substations involving 2,000 Mvar
of compensation capacity in series in 500 kV lines and more than
5,000 Mvar of inductive compensation in parallel.
Revisions were also made in the Emergency Control Schemes in the
areas under influence of the new installations, specifically,
studies related to steady state performance, dynamic performance
and electro-magnetic transients.
PROJECT
13
Development
of Systems for
Disturbance Analyses and Intervention Management
The Project deals with development of infrastructure used in the
disturbance analyses and intervention management – SGI procedures.
The objective of the disturbance analysis process is the implantation
of an automatic system for receiving recordings of disturbances
originating in Agent short-term oscilographic networks. A pilot
computational system for accessing data in the FURNAS oscilographic
network is being implanted at this time.
The process of intervention management aims at the development
of a computerized system that will allow ONS to administer and
control the intervention processes and permit Access by ANEEL
and sector agents to all pertinent information in the project
systems.
The SGI Intervention Management Project was concluded in the first
half of 2003 and is now in the final testing stages before implantation.
Tests conducted together with Agents have identified the need
for some improvements which will be made in 2004.
PROJECT
14
Improvement of the Transmission
Administration Processes
This
Project aims at improving the processes related to the definition
of the expansion of the inter-regional interconnections, to guarantee
the electric energy reliability and quality standards, management
of the transmission contracts and settlement of monthly charges
for the use of the transmission system.
Some of the important results already achieved: conclusion of
the computerized system used for the management of transmission
contracts; edition of the geo-electric map updated to 2006; the
improvement of the methodology used for reliability analyses in
the Expansions and Reinforcements Plan; improvements of the parameters
for the long duration loading of transmission lines and transformers
and the ongoing development of systems for management of the quality
of energy.
PROJECT
15
Improvement
of the Resources
for Real Time Operation
This Project was designed to provide ONS with conditions to be
able respond with increased speed and safety, to the demands of
real time operation. Works contemplates the perfecting of supervision
and control tools, improving the analyses processes of real time
events and generally improve the infrastructure at the Operation
Centers.
New procedures were implanted to provide data for the settlement
of transmission contracts and furnish information to the wholesale
market – MAE - Supervision and control systems at Operation
Centers were improved by modernizing hardware at these Centers.
Other upgrades were made to improve the telecommunications resources
used among the Centers. Two important data bases were integrated
– the Technical Database and the Real Time Database. The
Operations Training Simulator was also set up in 2003. A new software
program – a pilot version of the Network Power Flow Analysis
Program – was implemented as well as the Ground Fire and
Atmospheric Electric Discharge Detection System. Finally, the
ONS Operation Centers all passed ISO 9001-2000 certification after
the modernizing of their infrastructure.

This
section covers the main activities included in the daily ONS work
routine and the most relevant results achieved in 2003. In some
cases, specific on-demand work requested by other sector entities
will be mentioned even though this work is not seen as part of
the normal daily activities.

5.1.1
Relations with Government, Regulatory Agencies and Sector Entities
In
2003, the process of information exchange between the National
Operator and Government, Regulatory Agencies and other sector
entities was conducted within the established rules for such activities
resulting in major advances in the formation of institutionalized
procedures. As such, not only the routine products at ONS, as
specified in the Grid Procedures, as well as the products resulting
from outside requests, were all issued in their designated time
frames and served as the basis for many decisions made in the
various segments of the electric sector.
Relations with the Government, specifically the Ministry of Mines
and Energy, were highlighted by the following events: the presentation
of subsidies, by ONS, to the government to support the monitoring
functions of the electro-energetic supply conditions program.
Among these important subsidies was information concerning the
urgent need to overcome adverse conditions in the South due to
greatly reduced water levels at reservoirs in the period extending
from September to December and the elaboration of Risk Aversion
Curves for the region. In the Northeast region, the period of
September to December was the driest in the historical database
and demanded the adoption of special operative management measures
by ONS. To help contain the situation, additional thermal dispatch
was ordered. Special interchange energy management programs were
implemented, complemented by a reduction of the lower limits for
acceptable water outflows in the region, authorized by the ANA.
All these efforts were coordinated in harmony with the various
sector and governmental entities in order to overcome the difficulties
witnessed in the system until the hydrologic situation returned
to more favorable conditions.
Regarding the relations maintained with ANEEL in 2003, mention
must be made of the technical work done by ONS at the instruction
by this agency in order to support its regulatory functions related
to the administering of public auctions and authorizations for
reinforcements and expansion o f the transmission system. The
objective of such work was to create structural solutions to guarantee
the operative electric safety of the NIS.
When looking at the question of the management of systemic difficulties,
to maintain the high standards of energy supply, the Regulator
did act promptly designing regulatory measures for all the special
actions adopted to overcome the problem. In this vein, an important
evolution was made in the implantation of mechanisms such as the
Risk Aversion Curves in the sectorial methodology, which on one
side, integrated the criteria in the energetic optimization models,
and on the other - aided the refinement of the premises and rules
for the usage of the Curves as an external instrument to the models.
Relations with the National Water Agency – ANA were highlighted
by the work articulated with ANEEL that is being conducted for
the revision the natural inflows increasing the reliability of
the hydrologic database based on accurate measurement of the water
stored at the reservoirs. Besides this work, with the growing
demand related to the multiuse of water, ONS was intensely active
supporting the Agency in seeking solutions to questions related
to the use of water at the reservoirs such as at Caconde on the
Pardo River and the reservoirs in the Paraíba do Sul River
basin, in order to assure an adequate water supply to the metropolitan
area of Rio de Janeiro. Regarding these activities, there is a
strong interaction between the ANA and the Basin Committees. Interaction
with the ANA was also intense during some periods in 2003, with
the equationing of the supply risks in the Northeast region. The
Agency flexibilized the outflow limits at the reservoirs at Três
Marias and Sobradinho, located in the São Francisco river
basin.
Regarding relations with MAE, routine contacts throughout 2003
included the furnishing of data, information and versions of computational
programs designed for operation optimization. One of the highlights
worth mentioning was the implantation of the billing measurement
network which is accessed by both ONS and MAE.
Relations maintained with Agents and sector Entities were definitely
improved with the investments made to create formats of reports
that are more readable, without loss of technical quality or content
Access to data via the Internet web site created by ONS and direct
mailing lists. These resources reduced the number of requested
meetings and individual presentations while also enhancing the
quality of the meetings eventually held.
In 2003, mainly targeting new Agents, ONS issued a compact publication
entitled "Agents Manual” offering a transparent vision
of the steps to be taken by Agents and by ONS when integrating
new installations in the NIS.
Parallel to this work, investments were made for developing internal
processes at ONS used to conduct institutional relations with
sector Agents aiming at harmonizing actions taken by both parties.
Besides the institutional relations maintained with Agents, the
operative relation is considered equally important, especially
for conducting short-term and real time processes. In this respect,
mention should be made of the operational instrumentation created
at the National Operator to allow data and information to flow
at a great speed while still allowing for the verification of
the quality of content. Other efforts were made to improve management
of relations designed to approximate Agents to ONS through events
such as meetings, events and visits in order to solidify the interface,
functional and operative, between ONS and sector Agents.

5.1.2
International Relations
Although
the National Operator is exclusively focused on the Brazilian
Electric Sector , relations with other entities overseas do exist
and among the important events recorded in 2003, we cite:
•
As an associate member of the Electric Power Research Institute
(EPRI) - the National Operator was able to access special computer
applications, mainly used for operation planning and real time
operation.
• As an affiliate of The Group of International Comparison
of Transmission System Operation Practices – an international
organization that congregates 20 independent electric system operators
- ONS supported the “2003 TSO Workshop" held in Rio
de Janeiro. ONS participated in five taskforces – one for
each phase of operation. Participation included planning to post-operation,
always looking to identify benchmark models, seeking international
references for improving technical and corporate functioning –
ONS is the one and only independent system operator in Brazil.
• Continuity was given to the work underway on the Argentina-Brazil
Agreement concerning systems operation - ONS and CAMMESA held
meetings of a techno-managerial nature with the participation
of the technical Directors of both entities. The results were
positive: enhancement the operative processes already in use,
mainly in the energy exchange programming area used by Argentina,
through the conversers located at Garabi I and II; reducing transmission
constraints associated with energy importation and exportation
between the two countries; new studies for short and mid-term
operation planning and improved flow of information between ONS
and CAMMESA.
• In its final year, the partnership with US Energy Association
(USEA), financed by the USAID, ONS received a Technical Mission
from CAISO (California Independent System Operator). Presentations
of great interest were organized for the technical body at ONS.
A trip to the US was also made by ONS representatives earlier
in the year, to California for visits with CAISO and PG&E.
Special areas of interest were discussed such as; Information
Technology, Agent Relations, Use of Information Systems, Computer
Programs - used by CAISO for conducting electric studies, Load
Forecasting, Maintenance Management and IT Strategies for System
Safety. Negotiations are underway to extend funding throughout
2004 for this partnership.
5.1.3
Relations with Society and the Press
In
2003, ONS marked its presence at various technical seminaries,
public events and work meetings held with authorities and entities
from the organized society in which the details of the electro-energetic
supply conditions were elaborated among other management aspects
related to the NIS
The
ONS web site was an important source of information and received
many enquiries not only from sector Agents but from the press,
research organizations and the public at large. More than 800
visitors a day were recorded, higher than the 700 per day registered
in 2002.
The
National Operator maintained almost permanent contact with the
Press regarding the operative conditions of the NIS in 2003, not
only through the divulging of information at the web site but
in attendance of specific enquires made by other means. In 2003,
ONS was cited nominally in more than 673 articles published in
national newspapers. Roughly 86.9% of the comments made were positive.
In terms of volume, these articles were enough to fill 148 newspaper
pages.
The National Operator image, as a provider of reliable, updated
technical information, in matters related to the National Interconnected
Electric System, was confirmed as being very positive in a survey
conducted by the ABDIB (Associação Brasileira da
Indústria de Base), in July of 2003. The survey was made
among executives from the electric sector and generally concluded
that the Operator is the most highly reliable entity in the sector.

5.2.1
Improvement of the Management Model
Because
of the specific nature of its institutional functions and the
many roles played, ONS decided to improve its Management Model
to better its performance related to both institutional and organizational
activities.
In 2003, the executive direction, managers and technical teams
at ONS undertook many projects involving significant investments
made in designing new management polices at the Operator. The
first step was to identify and to begin discussion on corporate
institutional prerogatives, their nature and characteristics and
company principles and organizational values and ethics. This
lead to the understanding that it was necessary to conceive and
implant new organizational instruments that were given the name
– Organizational Systems - all aimed at improving intercorporate
integration and the capacity to coordinate internal and external
actions at ONS.
The development of the Organizational Systems included special
targets such as: the Human Resource Area, Grid Procedures, Technological
Development, Knowledge Management, Relations and Communication,
Products and Processes and Corporate Financial and Economic Planning.
In 2003, more than 180 professionals were actively involved in
these projects. For each one of these systems, strategies were
developed to viabilize the implantation of new procedures and
resources for implantation in 2004. Special emphasis was given
to the establishing of performance indicators for the actual organization
in order to gauge progress (see details further on).

5.2.2
Dimensioning the Workforce
By
the end of 2003, ONS concluded the studies for the redimensioning
of its employee body that remained stable since 1999, in spite
of the ever-growing workload resulting from the expansion of the
Agent population and the physical assets of the NIS. These factors
were not taken into consideration when the size of the workforce
was first studied. Conclusions clearly showed a need to increase
the staff by 17%. In the first step of the redimensioning, the
Executive Directory authorized a first increment of 12 % in 2004
and a subsequent complement over the short term. The addition
of new human resources was approved by the ONS Administrative
Board and later approved by ANEEL in 2004.
5.2.3
Human Resource Development
Capital
resources of R$ 1.4 million were applied in personnel training
and development programs – a value equivalent to 2% of the
payroll. In 2003, 398 employees participated in training programs
representing 77% of the workforce.
The programs were offered in response to knowledge gaps identified
by the Operator, and from requests made by the actual professionals
at the organization. Some courses were given under agreements
maintained with federal universities such as Itajubá, Santa
Catarina and Rio de Janeiro.
To complement the professional formation programs, joint training
events were held with other electric sector entities held in other
state capitals around the country. These programs covered topics
such as the operative safety of electric systems, sector economy,
system protection schemes, and power quality – themes all
considered vital by the Operator in view of their strong systemic
character and the daily technical activities always focused on
all these issues. This initiative, not originally foreseen in
the functions of the Operator, fulfilled a gap left in the electric
sector since it’s restructuring when sector companies began
to progressively reduce their technical teams.
The renewal of technical personnel is seen as a necessity in view
of the fact that the average age of the present workforce is 41
years – 16% of employees are more than 51 years old –
a continuous renewal program at the Operator is just good strategy.
In this context, in 2003 a “Junior Employees Development
Program” was instituted at ONS. The objective is to prepare
the younger professionals to become specialists in their respective
work areas, be it technical or administrative.
In 2003, the Operator also concentrated on 29 Trainees –
20 university graduates and 9 with technical school formation
– all in the 25 year age range. The Trainee Program includes
a job rotation scheme among various work units at ONS –
their individual performance is evaluated with an eye on their
possible contracting by the Operator or the electric sector workforce.
Additionally, 22 university students were offered 1-year apprenticeships
in order to source potential new talents for ONS and help prepare
these young people for the general job market-place.
Last year, special training courses and programs were created
and offered to managers, supervisors and selected employees who
eventually substitute these positions.
Considering the importance of system operator qualification, in
2003 ONS concluded the adaptations made to the Operator Training
Simulator purchased from
the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI). The modifications
were made by CEPEL and the equipment should be placed in operation
by the first quarter of 2004.
5.2.4
Improvements of the Information and Telecommunications Infrastructure
Within
the activities developed in the Information and Telecommunications
areas, the following events are highlighted:
•
Continuity of the structuring, integration and launching of the
primary and operational Technical Database at the ONS Operation
Centers.
•
Implantation of strategic complementary back-up information system
for use by the corporative and operative areas of the Operator.
•
Consolidation of the telecommunications infrastructure, incrementing
the quality and reliability of corporate and operative communication
flows through the upgrading of recording systems at the Operation
Centers and the expansion and updating of the central telephone
desks.
•
Analyses of contingency occurrences resulting from major outages,
minimizing the risks to the operation of corporate systems at
the company. This initiative was made to flexibilize the IT and
telecommunications resources when faced with large disturbance
scenarios that could interrupt the use of some installations.
•
Consolidation of the present version of the Peoplesoft corporate
management software program and the migration to a newer version
of this same program will be concluded in 2004.
•
Improvements made to the telecommunications resources, upgrading
voice and data flow networks used at the Operator. In the first
phase, the Operative Network (ROP) was consolidated followed by
the Operation Support System (RAOP) that permits interconnection
between the Operation Centers at ONS and those owned by third
parties. The second phase – improvements will be made to
both aforementioned systems, expanding interconnections to include
substations, plants and information concentration points between
Agents and the Operation Centers.
•
Technological updating of communication protocols used to interconnect
the Operation centers to the network installations. ONS, together
with the Agents and CEPEL, realized an important Project in this
context that resulted in the implantation of the transport protocol
- TCP/IP. This work helped overcome a series of limitations that
interfered with information exchanges between the Centers. In
the near future a new protocol will be implanted – the Inter-Center
Communication Protocol (ICCP) – developed for the National
Operator and third party operation centers. The implementation
of this protocol will raise the standard of protocol efficiency
to the IEC international norm and provide more flexibility in
the construction of tables used for cross-referencing data transferred
between centers.
5.2.5
Performance Indicators
In
2003, the definition and implantation of the corporate performance
indicators was concluded. These indicators cover the following
areas: General Corporate Services Administration, Financial Management,
Human Resources, Information Technology and Telecommunications.
In regard to the indicators developed for measuring the performance
of the Main Transmission Network, in compliance with the Grid
Procedures, ONS initiated the collection of data and calculation
of some of the indicators needed to create a realistic vision
of the behavior of the Main Transmission Network.
ONS defined and formulated indicators that will measure the performance
of the operative processes and the quality of its products. Among
the indicators that were defined are those used to evaluate the
results of ONS work as perceived by society. These indicators
are receiving priority treatment to speed up their finalization.
The set of 41 indicators under development may be grouped into
the following macro-functions:
| Electro-energetic
Supply Follow-up |
5
indicators |
| Energy
Quality Supply Evaluation |
4
indicators |
| Programming
Effectiveness Evaluation |
5
indicators |
| Recommendations
Compliance Evaluation |
6 indicators |
| Supply
Reliability Evaluation |
7
indicators |
| Energy
Supply Low-Price Evaluation |
4
indicators |
| Corporate
Performance Evaluation |
8
indicators |
| Institutional
Evaluation |
2 indicators |
5.2.6
Technological Development
Because
of the responsibilities and vision of ONS of the systemic operation,
in 2003, the National Operator made organized efforts prospecting
for developing new technology projects.
Supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology - (MCT/FINEP),
ONS launched five technology development projects in collaboration
with the Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC), the University
of São Paulo (USP), the University of Campinas (UNICAMP)
and the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ). The total
value of the projects, all of which are part of the ONS Action
Plan, ranged in the order of R$ 7 million. The projects were conducted
to introduce innovations to enhance the systemic environment of
the Main Transmission Network and improve the Operation Planning
and Programming models in place.
In 2003, ONS maintained association with EPRI and associated with
LACTEC.
On another front, ONS made a proposal which was accepted by the
other operator-associates of the Group of International Comparison
of Transmission System Operation Practices" (TSO) to include
on the group’s organizational agenda, as permanent themes,
“Technology – Acquisition, Evaluation of Results and
Technological Prospecting “, issues to be regularly discussed
at all TSO encounters and meetings.

The
integration of New Agent Installations in the NIS involves responsibilities
belonging to ANEEL, ONS and the Agent, owner of the new installation
in question, and finally, other Agents integrated and/or connected
to the Main Transmission Network whose operation may in someway
be affected by the presence of the new installation.
During 2003, new installations were connected to the generation
and transmission segments belonging to new Generation, Transmission
and Free Consumer Agent categories.
With an eye on correct integration procedures for new NIS operation
installations, ONS conducted a series of studies and analyses
together with Agents, in order to guarantee the safety, quality
and reliability of the energy supply of the Interconnected System
and Agent installations. All studies and related activities and
analyses were conducted within the strict observance of guidelines
laid down or authorized by the Grid Procedures.
In all, 59 test programs were run for the coordination and programming
of new equipment, generator units, transmission lines, special
schemes, CAG Automatic Generation Control programs and installation
re-arrangements.
In
compliance with the specific directives issued by ANEEL concerning
the integration of new work in the System, ONS developed additional
activities as follows:
•
The Operator established, as per Official Communication SRT164/02,
a system for issuance of Access Approval Term for transmission
installations based on the verifying of compliance of all pre-defined
conditions including the conceding of the concessions, contractual
conditions, recommendations made on pre-operational and commissioning
studies protection studies and the requirements laid out for systems
of supervision and telecommunication according to Grid Procedures.
In this context, 105 Access Approval Terms were issued in 2003
authorizing the integration of new transmission installations
in the Main Transmission Network. The following highlights are
among the 5,000 km of new T lines that went on-line in 2003:
•
Interconnection of the Southeast / Northeast - 500kV T line between
Serra da Mesa and Sapeaçu and integration with the existing
system in the Southeast Governador - Mangabeira region; 3rd interconnection
circuit of the North / Northeast region, 500 kV T line - Tucuruí
/ Açailândia / P. Dutra; 2nd Southeast / South interconnection,
500 kV T line - Ibiúna - Bateias double circuit; conversion
to 500 kV of two 230 kV circuits in the P. Afonso / Fortaleza
axis; first steps of the implantation of the 2nd circuit in the
Southeast / North interconnection - LT 500 kV T line with energization
of the Serra da Mesa / Miracema T line section.
Regarding generation units, approval processes were also issued
by ANEEL, regulamented by Resolution 433, dated 08/26/2003, and
ONS through declarations authorizing the beginning of tests and
commercial start-up of the production units. A total of 23 Grid
Procedures compliance declarations were released for 16 thermal
plants and 7 hydroelectric plants. An additional 24 compliance
declarations were also issued by ONS for small hydroelectric plants
that were connected to the system from outside the Main Transmission
Network.


The
National Operator, in the management of electro-energetic resources,
always follows Grid Procedures, and the prevailing techno-economical
conditions of the system, maintaining the lowest possible cost
profile while preserving the safety of the operation, not only
under normal operative conditions but also in the face of contingency
events. Highlighted in the activities linked to this area are
included: the commissioning of new installations - generation
and transmission - before their integration with the NIS that
require maneuvers and interventions in the transmission network
and re-managing of generation in order to guarantee the continuity
of the power supply at these times.
The instrument used by ONS to evaluate and monitor the safety
conditions of the energy supply is the Biannual Risk Aversion
Curve – CAR, as defined and based on the work program for
generation and transmission indicated by ANEEL, the forecasted
market and the hypotheses to be verified, of the critical hydrologic
conditions in the two-year being analyzed. This Curve indicates
and establishes, for each region, the minimum levels of required
equivalent water storage at the reservoirs in the system, throughout
each month, over a two-year horizon, so that the water resources
will assure attendance of the needs of the electric energy market.
In
2003, the favorable hydrologic conditions in the Southeast /Midwest
regions helped to complement the amounts of exported energy –
from the North to the Northeast - maximizing the energy exchange
to this region. Through this measure, it was possible to supply
nearly 20% of the load for the Northeast region by minimizing
the use of the region’s water resources and proportioning
a water storage gain of 30% capacity at the reservoirs located
in this region.

In the case of the Northeast region, with the worsening of the
hydrologic conditions over the last few months of 2003, specific
measures were taken by ONS together with SEN/MME, ANEEL and MAE,
that resulted in the ratification by ANEEL, for the use of preventative
thermal dispatch under circumstances that would imminently violate
the CAR value established for the region based on the horizon
outlined in the Monthly Operation Program, starting in the month
of December or 2003.
At
the same time, interactions among ONS, MME, MMA, ANEEL, ANA and
CHESF, resulting in the issuance of Resolution ANA-434 dated 12/09/2003,
reducing the minimum outflow from 1,300 m3/s to 1,100 m3/s at
Sobradinho, with the objective of allowing for greater energy
reception from other regions and/or greater thermal dispatch in
the actual Northeast region. New agreements were also initiated
involving ONS, MME, ANEEL and Petrobras, related to increasing
the availability of natural gas to the thermal plants in the region.
In the South region, significantly reduced inflows to the region’s
main reservoirs, mainly in the second half of 2003, influenced
the work at ONS to determine increased energy transfer amounts
to this region and implementing special Emergency Control Schemes
- ECE, at the substations - Ibiúna and Bateias- in order
better explore the transmission network and at the same time,
preserve the safety profile of the NIS.
This scenario was particularly severe at the plants located in
the Uruguay and Iguaçu river basins, forcing the storage
level to only 15% EARmax, which resulted in the shutdown of the
Machadinho hydroelectric plant.
The situation obliged ONS to create a special electro-energetic
operation strategy for the South region, built around a water
storage priority at the plants located in the Iguaçu river
basin, to preserve electric safety and avoid load supply deficits
in this region in the period of October and November of 2003.

Efficient
management of the transmission network allows for the attendance
of the load demand at the main consumer centers while maintaining
the goals for energetic optimization and recovery of the water
storage levels through the energy transfer among the various regions.
At the same time, transmission management aids in the administering
of programmed interventions needed for maintenance purposes as
well as those needed at the time of integrating new installations
in the System to safeguard the operational safety of the NIS.
In 2003, more than 13,400 requests for shutdowns and interventions
were received and analyzed by ONS – nearly 20% more than
the number processed in 2002.
Other activities were highlighted – the actions taken to
handle contingency situations that provoked forced shutdowns of
equipment and subsequent coordination of maneuvers / interventions
in the transmission network and re-management of the generation
programs in order to guarantee the continuity of the energy supply
even under these extreme conditions. An example of such a situation
was the collapse of 19 double circuit towers in the 440kV Jupiá
– Bauru transmission line at the end of 2003. This event
did not interrupt the load supply thanks to the safety scheme
arrangements that were in place and the modifications that had
been previously introduced at the substations in the area.
The management of the transmission network allowed for the necessary
sectioning of the Main Transmission Network required at the time
for the entry into operation of large trunks without provoking
any supply interruptions.
Finally, ONS transmission management included the elaboration
of technical reports on the transmission network attendance capacity
in the face of new load requirements arising from the surplus
energy auctions held by MAE that allowed the supplying of more
than 912 MWmed throughout the NIS – a Project developed
at the Operator at the special request of the Ministry of Mines
and Energy.

In
2003, ONS participated in joint actions together with the ANA,
ANEEL, Agent-owners of system installations and other entities
involved with the management of hydrologic resources at the river
basins where production plants are located in the NIS, in order
to preserve and optimize the use of this precious asset.
Highlights during the year’s activities include the special
management scheme developed for the Paraíba do Sul river
basin, where two important issues demanded attention. The first
was how to avoid the aggravation of the unfavorable water conditions
that were being registered. ONS elaborated studies together with
other government organs and entities responsible for the basins.
These groups furnished valuable information to create regulatory
guidelines - by ANA - and new hydrologic operative constraints.
The second matter was related to the ecological and environmental
problems that resulted from the discharge of pollutants into the
Pomba River, an affluent of the Paraíba do Sul river system
- the situation was overcome by using water reserves stored at
upstream reservoirs to flush out the affected area.
Special mention must be made of an important study entitled the
Natural Water Flow Series Revision that was developed along the
year and included the eight main river basins in Brazil. The focus
was on energy generation in the Grande, Paranaíba, Tietê,
Paranapanema, Iguaçu, Paraná, São Francisco
and Tocantins river basins. The basins contemplated in the study
represent more than 2.2 million square km and contribute 91% of
the natural energy inflow in the NIS. The series of annual inflows
were evaluated and incorporated with studies of the multiuse of
the water resources by seasonal period, subsystems and type of
activity practiced in the various regions. The Project was supervised
by a Special Commission formed by technical personnel representing
ONS, ANEEL, ANA and the CCPE/MME with the participation of the
Generation Agents involved in their respective basin areas.

In
2003, the real time operation of the NIS was conducted under conditions
considered normal without registering any major disturbances.
Actions implemented by ONS and by sector Agents, to reinforce
the operational electric safety of the System were based on experience
acquired in previous years where large disturbances did occur
– this background helped to minimize the consequences of
the disturbances that were in fact recorded during the year 2003.
This positive performance was achieved based on the creating of
norms and procedures and the processes introduced in the daily
Operation and Post Operation Programming that decisively supported
the actions and decisions made at the ONS Operation Centers.
Regarding the elaboration of norms and procedures, more than 1,330
Operation Instructions were issued including Operational Routines,
Technical References, 431 Operative Messages and 397 Operational
Diagrams – an average increase of 22.6 per cent in comparison
with the previous year’s verified volume.
Results of the coordination and operation analyses, together with
sector Agents, of the Operation Programming in 2003 shows the
following numbers: 37,042 interventions in the components of the
Operation Network, with and without shutdowns. Of this total -
30,376 were programmed representing an increment of 2.9% in relation
to 2002. The remaining 6,666 interventions were characterized
by emergency conditions which represented an increase of 29.6%
over the previous year.
In the post operation stage, the numbers were also expressive
of the intense work done by ONS over the year: 126 Preliminary
Operation Reports - RPO, six Operation Analysis Reports - RAO
and 38 Disturbance Analyses Reports - RAP, all showing decreases
of the orders – 13.7%, 14.3% and 7.9% respectively, in relation
to 2002. Mention should be made of the organization and operalization
of the data used for settling financial accounts at MAE and for
the verifying of information used in the transmission contracts.
There was significant evolution in the elaboration of the Technical
Data Base at ONS, an instrument used in various processes at the
Operator. In 2003, more than 130 thousand recordings were entered
making this reference resource even more efficient for all users.
Among the activities engaged in, to help upgrade the ONS Operation
Centers, highlights include the modernization of the hardware
and software resources in the control rooms aiming at increasing
the ability to observe, monitor and control events in the NIS.
This was done by incorporating powerful simulation programs in
real time through latest generation computer applications. Improvements
were also made to the physical assets at these Centers to ease
the work by the system operations technicians.
With this same objective in mind, the OTS – the Operation
Training Simulator – underwent the final installation stages
at the CNOS Operation Center. This equipment is manned with a
SAGE software program designed to support real time training activities
for teaching operators to deal with the extreme situations provoked
by major disturbances as they happen. This learning tool will
be implanted at the other Operation Centers at ONS.
5.7.1
Supervision and Control Systems
at Operation Centers
In
2003, an important cycle of development was consolidated at
all Operation Centers at ONS. Some highlights include:
•
Issuance of the Temporary Acceptance Certificates for the Northeast,
North and South – COSR-NE, COSR-N and COSR-S, Regional Operation
Centers, developed with technology purchased from ALSTOM. These
centers have all the tools needed for conducting network analyses,
operator training simulations and recording and processing of
historical information. Resources are also available for the Automatic
Generation Control which will allow ONS to fully assume control
of the North Region through the COSR-N Control Center.
•
Modernization of the hardware at the Southeast Operation Center
with the substitution of the application servers. This will make
available, sufficient computer resources for the integration of
new Agents at this Center.
•
Modernization of hardware at the National System Operation Center,
substituting the application servers for the Itanium equipment.
The adaptation of the applications is forecasted for conclusion
in the first quarter of 2004.
•
Integration of the generation system Real Time Data Base at the
CNOS with the ONS Technical Data Base, reducing the efforts expended
to collect data and the incidence of convergence of information
in only one data base source.
•
Intense usage of real time tools proportioned by the new Control
and Supervision System – SSC, by the real time operator
teams, such as Network Analysis that allow for the evaluations
of shutdown requests and the safety conditions of the System.
•
Utilization, by all ONS Centers, of resources for accompanying
ground fires and electric atmospheric discharges. This system
will be improved gradually by systematic work underway for obtaining
geographic coordinates of all transmission towers and by the improving
of detection algorithms and alarm systems.
5.7.2
National System of Control
and Observation - SINOCON
Ongoing
work of the SINOCON in 2003, in strict collaboration with sector
Agents, included the following activities:
•
Definition of the installations included in the Emergency Phase
of the Project - this resulted in the formation of a group of
153 plants and substations. Of these, 117 will have their control
and supervision equipment substituted or implanted for the first
time and 36 installations will have their existing equipment upgraded.
To promote competitiveness among the proponent suppliers, a public
tender was edited for the supply of goods and services needed
at the 117 installations, divided into 4 supply lots.
•
Purchase process management answered 292 questions forwarded by
all potential suppliers. Commercial and technical proposals were
received for the four different purchase lots. The bidding procedures
for the first three lots should be concluded in March of 2004.
•
Contracting effected for the supply of goods and services of the
first 13 of 36 installations.

5.7.3
Operation Centers Certification
The
ONS Operation Centers were re-certified according the NBR ISO
9001 Version - 2000 Norm, after having been submitted to external
auditing done by Bureau Veritas Quality International (BVQI).
The Centers that had previously qualified for only Real Time Operation,
under the ISO 9000:1994 Norm, are now fully certified for all
processes that make up the Quality Management System certification
as per the revised version of the ISO Norm.

To
guarantee the NIS operative electric safety, ONS has been dedicating
all efforts with great zeal to the prevention of situations of
potential risk to the interruption of the energy supply, adopting
measures that impede the occurrence and/or propagation of sudden
shutdowns of equipment during disturbances and speed up the reestablishing
of the interrupted loads in the System. These efforts are focused
on increasing the NIS capacity to support the presence of multiple
contingencies.
In this context, in 2003 the process to consolidate the Recommendations
for Management of the ONS Analyses Reports of the electric occurrences
and disturbances was made, implanting a follow-up system with
an interface for all Agents via the Internet. This initiative
is guaranteeing control of the implementation of the measures
recommended to avoid reincidence of the problems identified in
the analyses reports and consequently, the minimizing of the consequences
of disturbances in the NIS.
In 2003, thirty eight RAP – Disturbance Analysis Reports
were elaborated, together with involved sector Agents.
Among activities designed to increase NIS operative safety, a
total of 45 schemes were incorporated and 27 existing schemes
were revised, due to the expansion of the G and T systems.
As a result of actions already implemented or underway in 2003,
the following large disturbances were recorded. These events did
not provoke discontinuity of the energy supply to the System:
•
• August/2003 – total loss of the SE Itaberá
750 kV resulting from the automatic shutdown of six connecting
transmission lines;
•
• September/2003 – simultaneous loss of four 750 kV
transmission lines associated to the SE Itaberá;
•
• December/2003 - total loss of the SE Bauru resulting from
the automatic shutdown of 10 440 kV transmission lines and two
440/138 kV transformers.
Another important aspect has to do with the NIS integration involving
large installations that entered into operation without causing
any negative impact in the System thanks to the work and studies
conducted beforehand to defend the electric safety of the NIS
and the installations of the new connecting Agents.
In November of 2003, the 1º Cycle of Debates (CINTER) was
held at ONS. The theme “Interconnected System Safety”
was treated by specialists at ONS who presented results from studies
and then debated new proposals for measures to be taken to impede
disturbances or when impossible to avoid, reduce their impact
on final consumers.
Looking at the applications used in programming and in real time
operation, to assure electric safety in the NIS, the following
highlights were registered in 2003:
a)
AGORA System
A pilot system is being implanted of the AGORA (Advanced Grid
Observation Reliable Algorithms) System. This will be used to
evaluate system functions. The main characteristic of this system
is to use a direct method of analytic problem solving to examine
power flow rather than a system dependent on successive approximations.
This allows reaching consistent solutions in a greatly reduced
processing period, and increasing the possibility of including
new functions in the analysis such as recomposition and the search
for corrective measures in real time, either under normal operation
conditions or in contingencies. All acceptance testing in real
time was run and concluded with success. The system is now ready
and available for use.
b)
Electro-mechanical Stability Programs
The year 2003, witnessed the beginning of the development and
implantation of a program to evaluate the voltage and dynamic
stability of the NIS in real time. This program was named ORGANON,
developed by BC-Hydro-Canada, by a Brazilian professional who
at this time is employed by ONS.
This program, through a friendly man-machine interface, allows
the safety margins of the NIS to be defined at any given moment
of the operation. This is seen as a program vital to the reliability
of the electric operation since it is an instrument that focuses
on the area of greatest fragility in the Brazilian System –
that is the dynamic behavior – due to the system’s
characteristics of very long extra high tension transmission lines
interconnecting large hydro plants, long distances between each
of these plants and from load centers. The program proportions
many gains for the operational study activities, operation programming
and programming in real time due to its processing speed and ability
to analyze cases “automatically”.


At
ONS, the Transmission Administration conducted various activities
including the new access management processes, expansion of the
transmission system and administration of new and existing transmission
contacts which includes the settlement of charges for the use
of the Transmission System.
Technical studies were made on behalf of ANEEL, highlighting the
establishing of system performance indicators. The implanting
of the energy supply quality management system continued throughout
the year as well.
ONS played a relevant role in the development of the transmission
business model, used as a paradigm for treating the generation
segment in the new institutional model being designed and adopted
by the Ministry of Mines and Energy.
5.9.1
Expansion and Reinforcements
In
June of 2003, the Expansion and Reinforcement plan – PAR
was issued for the Main Transmission Network, for the period covering
2004/2006. Presentations and discussions were held to divulge
the Plan at Regional Seminaries involving sector entities and
Agents.
The projects proposed in the Plan represent investments in the
order of R$ 8.2 billion (about US$ 2.6 billion), and the incorporation
of 11,063 km of transmission lines of which 73% of the projects
have already been authorized by ANEEL or awarded at public auctions.
With regard to the expansion of the transformation capacity, recommendations
were made to implant an additional 21,431 MVA of which more than
54% has already been conceded in well defined concessions.
In the public tendering for new transmission installations in
the Main Transmission Network, conducted once again by ANEEL,
ONS was responsible for providing important technical support
in the elaboration of the actual tender documentation by developing
seven technical annexes related to the analysis of ten basic projects
for new installations, including the verification and compliance
of all technical content and processes with the established Grid
Procedures.
In response to a request from the Ministry of Mines and Energy,
ONS elaborated in collaboration with certain Agents, a detailed
report of the operative conditions of the so-called “ Other
Transmission Installations – DITs”, that are not part
of the Main Transmission Network, indicating the critical points
identified in relation their ability to supply energy to the market
. This work served as the basis for discussions with ANEEL that
eventually lead to the modification of existing legislation governing
the expansion of these kinds of installations – this project
is still underway at this time.
In response to requests from ANEEL, ONS held ten studies to evaluate
the impact of work delays on the performance of the NIS.
Among the important studies realized were the projects run together
with the CCPE to evaluate alternatives for energy supply to the
radial systems of the Main Transmission System. The Tables below
present the increments proposed in the Expansion PAR Plan for
2003/2005 regarding transmission lines and transformation capacity.
New
Transmission Lines for the Main Transmission Network - (Km)
Forecast for Implantation
| Voltage
kV |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
total |
| 230
|
1,336
|
1,198
|
440 |
2,974
|
| 345
|
370
|
238 |
342 |
950 |
| 440
|
- |
- |
3
|
3 |
| 500
|
928
|
2,105
|
1,628
|
4,661
|
| 750
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
| TOTAL |
2,634
|
3,541
|
2.413 |
8,588
|
New Transformation Capacity in the Main Transmission Network -
(MVA)
Forecast for Implantation
| Voltage
kV |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
total |
| 230
|
1,336
|
1,198
|
440 |
2,974
|
| 345
|
370
|
238 |
342 |
950 |
| 440
|
- |
- |
3
|
3 |
| 500
|
928
|
2,105
|
1,628
|
4,661
|
| 750
|
- |
- |
- |
- |
| TOTAL |
2,634
|
3,541
|
2,413
|
8,588
|
5.9.2
Access to the Main Transmission Network
Looking
at Main Transmission Network access processes underway in 2003,
32 new Access Reports were issued as well as 37 Process Revisions
– 17 from Generation Agents, 52 from Free Consumers Agents
and 2 others covering international interconnection requests.
The volume of reports issued was 37% higher than in 2002. The
Reports established the conditions for access connection to the
Main Transmission System, within the set of compliance details
as outlined in the Grid Procedures.
In
2003, revision was made of the Grid Procedures Module 3 entitled
“Access to the Transmission System” as a result of
the use first made of the Procedures by Agents and new requests
from various other Agents.
Furthermore, acknowledgment must be made of the efforts made to
integrate the Eolic Energy Plants with the support of the Ministry
of Mines and Energy that helped establish the conditions allowing
the integration of these plants with the generation networks,
members of the PROINFA.
The graph below presents the growth in the number of Access Request
Reports issued between 1999 and 2003.
5.9.3
Contract Administration and
Settlement of Transmission Charges
In
2003, 393 contracts were celebrated by the Transmission Administration
bringing the current total up to nearly 1,000 contracts signed
since the origin of this concept. This volume represented an increase
of 75% when compared to the number of contracts signed in 2002.
Additionally, highlight must be given to the implantation of the
computerized transmission contract management system and the development
of the new Ancillary Services Contract Model in compliance with
Grid Procedures Module 14 and the Official Communication 675/03-SRG/ANEEL.
Settlements of charges for the use of the transmission system
totaled 102, 444 transactions resulting in the issuance of Credit
and Debit Statements, relative to the authorized revenues for
the period in the amount of R$4.07 billion (about US$ 1.3 billion),
involving a total of 135 User Agents. It should be noted that
in relation to 2002, an increase of 37% was registered in the
number of Credit/Debit Statements issued in the period, a 40%
increase in the revenues allowed in the transmission segment of
the Main Transmission Network and a zero payment default rate
in 2003.
The
graphs that follow show the evolution of the increasing number
of signed contracts, the Credit and Debit Statements issued and
the number of Agents involved in these transactions:

5.9.4
Definition of Minimum Requirements for
Installations in the Main Transmission Network and Quality Indicators
In
2003, various studies were conducted. Among the most important,
mention must be made of the following: the development of the
criteria used for the checking of over-limit occurrences at circuit
breakers and associated equipment due to the increase in the relation
X/R in the NIS, the analysis of the reduction of short circuit
currents at the substations through the application of limit devices
to make viable the closing of the 345kV ring in the São
Paulo area, analysis of the viability of using mono-pole re-connection
in transmission lines of the Main Transmission Network and elaboration
of a proposal to introduce new requirements in the auction invitations
issued by ANEEL.
The work was done by a special group consisting of members from
ONS, ABDIB and ABRATE. Highlights include: work related to the
establishment of performance indicators for transmission lines
in the Main Transmission Network and a study of the statistical
distribution of the indicators as subsidies for ANEEL, used in
creating regulatory measures for the Variable Portion of the Transmission
Contracts.
Important strides were also made evaluating the quality indicators used in the Main
Transmission Network, especially those used to observe continuity at control points
on the frontiers of the T Network, directly related to the providing of energy transport
services. The performance of this follow-up process, first started in 2000, has
been greatly improved. Today the system consists of 702 control points under permanent
observation. The interruption Duration at Control points - DIPC was reduced from
2.8 to 2.2 hours per year, between 2000 and 2003. The Frequency of Interruption
at Control Points was equally improved over the same period, reducing from 1.6 interruptions
per year to 1.4.
|